“JUL 执行原理和流程”的版本间的差异
跳到导航
跳到搜索
Jihongchang(讨论 | 贡献) |
Jihongchang(讨论 | 贡献) (→日志原理解析) |
||
| 第11行: | 第11行: | ||
#Formatter 用来格式化 LogRecord | #Formatter 用来格式化 LogRecord | ||
[[文件:JUL 流程示意图.png|无|缩略图|814x814像素]] | [[文件:JUL 流程示意图.png|无|缩略图|814x814像素]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === 调试跟踪 === | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ | ||
| + | ! colspan="2" |Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("io.github.jihch"); | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! colspan="2" |return demandLogger(name, null, Reflection.getCallerClass()); | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !LogManager manager = LogManager.getLogManager(); | ||
| + | !manager.demandLogger(name, resourceBundleName, caller); | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !manager.ensureLogManagerInitialized(); | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !// Read configuration. | ||
| + | owner.readPrimordialConfiguration(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | // Create and retain Logger for the root of the namespace. | ||
| + | |||
| + | owner.rootLogger = owner.new RootLogger(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | owner.addLogger(owner.rootLogger); | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | !super("", null, null, LogManager.this, true); | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | |} | ||
2023年2月23日 (四) 08:25的版本
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1iJ411H74S?p=10
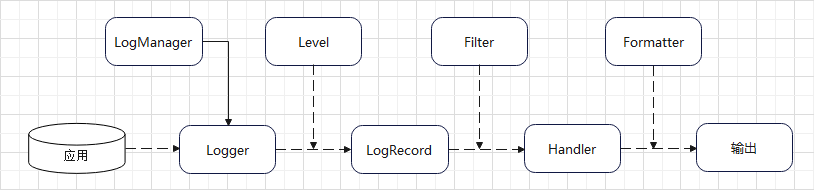
日志原理解析
- 初始化 LogManager
- Log Manager 加载 logging.properties 配置
- 添加 Logger 到 logManager
- 从单例 LogManager 获取 Logger
- 设置级别 Level,并指定日志记录 LogRecord
- Filter 提供了日志级别之外更细粒度的控制
- Handler 处理日志输出位置
- Formatter 用来格式化 LogRecord
调试跟踪
| Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("io.github.jihch"); | |
|---|---|
| return demandLogger(name, null, Reflection.getCallerClass()); | |
| LogManager manager = LogManager.getLogManager(); | manager.demandLogger(name, resourceBundleName, caller); |
| manager.ensureLogManagerInitialized(); | |
| // Read configuration.
owner.readPrimordialConfiguration(); // Create and retain Logger for the root of the namespace. owner.rootLogger = owner.new RootLogger(); owner.addLogger(owner.rootLogger); |
|
| super("", null, null, LogManager.this, true); | |