“使用 Redis 查询的一般程序实现和击穿、雪崩、穿透”的版本间的差异
Jihongchang(讨论 | 贡献) (建立内容为“1”的新页面) |
Jihongchang(讨论 | 贡献) (→布隆过滤器) |
||
| (未显示同一用户的25个中间版本) | |||
| 第1行: | 第1行: | ||
| − | 1 | + | === 最简单的一般实现 === |
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | package io.github.jihch.service; | ||
| + | |||
| + | import io.github.jihch.bean.ExpressInfo; | ||
| + | import io.github.jihch.exception.ClientException; | ||
| + | import io.github.jihch.mapper.ExpressMapper; | ||
| + | import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; | ||
| + | import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate; | ||
| + | |||
| + | import java.awt.datatransfer.Clipboard; | ||
| + | import java.time.Duration; | ||
| + | |||
| + | public class ExpressInfoService implements IExpressInfoService { | ||
| + | |||
| + | @Autowired | ||
| + | RedisTemplate redisTemplate; | ||
| + | |||
| + | @Autowired | ||
| + | ExpressMapper expressMapper; | ||
| + | |||
| + | /** | ||
| + | * 通过发货单查询物流信息 | ||
| + | * @param id | ||
| + | * @return | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | @Override | ||
| + | public ExpressInfo findByDeliveryOrderId(Long id) { | ||
| + | String key = "xushu-express:express-info:"; | ||
| + | |||
| + | //从 Redis 查询物流信息 | ||
| + | Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key + id); | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (obj != null) { | ||
| + | return (ExpressInfo) obj; | ||
| + | |||
| + | } else { | ||
| + | ExpressInfo expressInfo = expressMapper.selectByDeliveryOrderId(id); | ||
| + | if (expressInfo != null) { | ||
| + | redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key+id, expressInfo, Duration.ofHours(2)); | ||
| + | return expressInfo; | ||
| + | } else { | ||
| + | throw new ClientException("发货单:{} 的物流信息不存在", id); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }//end else | ||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
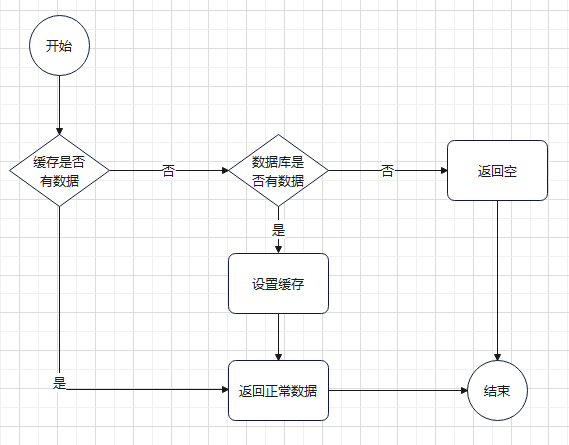
| + | [[文件:查询增加缓存实现的一般流程.png|居中|缩略图|569x569像素]]但这种一般实现,不足以应对高并发的场景,可能会出现缓存击穿、缓存穿透、雪崩的问题 | ||
| + | |||
| + | === 缓存击穿 === | ||
| + | 假设这样的场景:高并发情况下,像上面的这种一般实现,一个 key 一开始是不在缓存里的,或者它设置了失效时间在某一个时间点失效, | ||
| + | |||
| + | 但它又是一个访问频率非常高的 key,那么当大量请求密集访问这个接口的时候,就会出现因为缓存中没有这个 key,然后都去查询数据库,就会给数据库带来非常大的压力导致性能下降甚至崩溃。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== 解决方案 ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== 预加载缓存和设置缓存永不过期 ===== | ||
| + | 预加载缓存就是在数据被大量请求密集访问之前就提前设置到缓存中(比如节庆活动要访问的数据就在节庆活动开始前提前放进缓存),这样可以预防一开始 key 不存在时大量请求密集访问导致的缓存击穿; | ||
| + | |||
| + | 设置缓存永不过期就可以预防在 key 失效的一瞬间 大量请求密集访问导致的缓存击穿,但这样就要考虑要存储的数据量的大小和 redis 服务实例可以存储的大小,做好冷、热数据的区分处理,冷数据还是做定时失效,不然冷数据就会浪费缓存空间; | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== key 访问计数动态调整失效时间 ===== | ||
| + | 实际可能会有这种情况:就是我们没办法提前知道哪一个 key 会是热点数据,针对这种情况,我们可以为这些数据增加一个算法实现——计数单个 key 在单位时间内的访问频率,当高到一个阈值之后,我们把这个 key 设置为永不过期。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== 加锁排队 ===== | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | public List<ProductCategory> findProductCategory() { | ||
| + | String key = "product:product-category"; | ||
| + | Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (obj == null) { | ||
| + | synchronized (this) { | ||
| + | /* | ||
| + | 因为有可能存在这样的情况: | ||
| + | 请求A执行完了 | ||
| + | List<ProductCategory> productCategories = productCategoryMapper.selectProductCategory(); | ||
| + | 将要执行 | ||
| + | redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, productCategories, Duration.ofHours(2)); | ||
| + | 但还未执行 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 请求B(也可能是其他多个请求)执行完了 | ||
| + | Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); | ||
| + | if (obj == null) { | ||
| + | 将要执行 | ||
| + | synchronized (this) { | ||
| + | 但还未执行, | ||
| + | 就会出现多次 从数据库查询、更新到缓存的情况 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 所以进入 synchronized 一定要再查询一次 Redis,这样可以避免多次查询数据库、更新缓存 | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); | ||
| + | if (obj != null) { | ||
| + | return (List<ProductCategory>)obj; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | List<ProductCategory> productCategories = productCategoryMapper.selectProductCategory(); | ||
| + | redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, productCategories, Duration.ofHours(2)); | ||
| + | return productCategories; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } else { | ||
| + | return (List<ProductCategory>) obj; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight>既相对简单又比较彻底的方案还是加锁排队。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === 缓存雪崩 === | ||
| + | 是缓存中的 key 大量集中过期(或缓存服务器宕机),导致大量请求访问数据库,造成数据库瞬间压力过大,宕机。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 区别于缓存击穿的是:缓存击穿指的是大量并发请求集中访问一个 key 时,key 不在缓存里时出现的情况;缓存雪崩则是因为大量 key 在时间上集中过期或不存在时,面对大量并发请求的访问都要去查数据库时发生的情况。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== 解决方案 ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== 在加锁排队的基础上,设置随机失效时间 ===== | ||
| + | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | public List<ProductCategory> findProductCategory() { | ||
| + | String key = "product:product-category"; | ||
| + | Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (obj == null) { | ||
| + | synchronized (this) { | ||
| + | /* | ||
| + | 因为有可能存在这样的情况: | ||
| + | 请求A执行完了 | ||
| + | List<ProductCategory> productCategories = productCategoryMapper.selectProductCategory(); | ||
| + | 将要执行 | ||
| + | redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, productCategories, Duration.ofHours(2)); | ||
| + | 但还未执行 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 请求B(也可能是其他多个请求)执行完了 | ||
| + | Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); | ||
| + | if (obj == null) { | ||
| + | 将要执行 | ||
| + | synchronized (this) { | ||
| + | 但还未执行, | ||
| + | 就会出现多次 从数据库查询、更新到缓存的情况 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 所以进入 synchronized 一定要再查询一次 Redis,这样可以避免多次查询数据库、更新缓存 | ||
| + | */ | ||
| + | obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key); | ||
| + | if (obj != null) { | ||
| + | return (List<ProductCategory>)obj; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | List<ProductCategory> productCategories = productCategoryMapper.selectProductCategory(); | ||
| + | |||
| + | int seconds = (int) (Math.random() * 100); | ||
| + | Duration expire = Duration.ofHours(2).plus(Duration.ofSeconds(seconds)); | ||
| + | redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, productCategories, expire); | ||
| + | |||
| + | return productCategories; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } else { | ||
| + | return (List<ProductCategory>) obj; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight>实现让缓存失效的时间分散,就避免了缓存集中失效导致的缓存雪崩。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===== 缓存服务高可用 ===== | ||
| + | 实现缓存服务高可用,使用 redis 的哨兵模式,当某个 redis 实例异常、宕机时其他缓存服务实例迅速补位 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === 缓存穿透 === | ||
| + | 缓存中不存在、数据库中也不存在的数据,导致每次请求都会查询数据库,高并发访问这种数据的请求很可能是攻击者。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 比如发起 id 为“-1”的数据,或者 id 特别大(数据库中不存在的数据),导致数据库压力过大或宕机 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== 解决方案 ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== 缓存空对象 ===== | ||
| + | 这个方案就是使缓存中存储对应 key 的值为空(空字符串或其他代表空的值),查询缓存直接取到空值返回。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 这个方案的缺点就是如果查询的 key 值一直变的话,空 value 的缓存也会有很多占据缓存空间。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== 布隆过滤器 ===== | ||
| + | 这个是比较彻底的解决方案了,利用 bitmap 数据结构存储数据在数据库中是否存在的信息 | ||
| + | |||
| + | 如果 bitmap 返回不存在,那么就一定不存在; | ||
| + | |||
| + | 如果 bitmap 返回存在,那么就概率存在; | ||
| + | |||
| + | <u>注意:使用布隆过滤器需要在服务器启动阶段进行数据初始化加载,比如对于 id,在对外提供新增记录的功能前先将所有的 id 都加载到布隆过滤器中,之后每一次 insert 之后都要将 id 加入布隆过滤器。</u> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | redisson 中有对布隆过滤器的现成封装可以直接使用:<syntaxhighlight lang="xml"> | ||
| + | <dependency> | ||
| + | <groupId>org.redisson</groupId> | ||
| + | <artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId> | ||
| + | <version>3.16.1</version> | ||
| + | </dependency> | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight><syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
| + | public ExpressInfo findByDeliveryOrderId(Long id) { | ||
| + | |||
| + | RBloomFilter<Long> bloomFilter = redissonClient.getBloomFilter("xushu-product:bloom-filter:express-info"); | ||
| + | if (!bloomFilter.contains(id)) { | ||
| + | throw new ClientException("发货单:{} 的物流信息不存在", id); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | |||
| + | String key = "xushu-express:express-info:"; | ||
| + | |||
| + | //从 Redis 查询物流信息 | ||
| + | Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key + id); | ||
| + | |||
| + | if (obj != null) { | ||
| + | return (ExpressInfo) obj; | ||
| + | |||
| + | } else { | ||
| + | ExpressInfo expressInfo = expressMapper.selectByDeliveryOrderId(id); | ||
| + | if (expressInfo != null) { | ||
| + | bloomFilter.add(id); | ||
| + | redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key+id, expressInfo, Duration.ofHours(2)); | ||
| + | return expressInfo; | ||
| + | } else { | ||
| + | throw new ClientException("发货单:{} 的物流信息不存在", id); | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | }//end else | ||
| + | |||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight>也可以自行实现, | ||
| + | |||
| + | 注意:redisson 的开源版本没有做集群布隆过滤器的实现,pro 版本有要付费……https://redisson.pro/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === 参考 === | ||
| + | https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fb4y147qw/ | ||
2023年7月20日 (四) 05:56的最新版本
最简单的一般实现
package io.github.jihch.service;
import io.github.jihch.bean.ExpressInfo;
import io.github.jihch.exception.ClientException;
import io.github.jihch.mapper.ExpressMapper;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import java.awt.datatransfer.Clipboard;
import java.time.Duration;
public class ExpressInfoService implements IExpressInfoService {
@Autowired
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Autowired
ExpressMapper expressMapper;
/**
* 通过发货单查询物流信息
* @param id
* @return
*/
@Override
public ExpressInfo findByDeliveryOrderId(Long id) {
String key = "xushu-express:express-info:";
//从 Redis 查询物流信息
Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key + id);
if (obj != null) {
return (ExpressInfo) obj;
} else {
ExpressInfo expressInfo = expressMapper.selectByDeliveryOrderId(id);
if (expressInfo != null) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key+id, expressInfo, Duration.ofHours(2));
return expressInfo;
} else {
throw new ClientException("发货单:{} 的物流信息不存在", id);
}
}//end else
}
}
但这种一般实现,不足以应对高并发的场景,可能会出现缓存击穿、缓存穿透、雪崩的问题
缓存击穿
假设这样的场景:高并发情况下,像上面的这种一般实现,一个 key 一开始是不在缓存里的,或者它设置了失效时间在某一个时间点失效,
但它又是一个访问频率非常高的 key,那么当大量请求密集访问这个接口的时候,就会出现因为缓存中没有这个 key,然后都去查询数据库,就会给数据库带来非常大的压力导致性能下降甚至崩溃。
解决方案
预加载缓存和设置缓存永不过期
预加载缓存就是在数据被大量请求密集访问之前就提前设置到缓存中(比如节庆活动要访问的数据就在节庆活动开始前提前放进缓存),这样可以预防一开始 key 不存在时大量请求密集访问导致的缓存击穿;
设置缓存永不过期就可以预防在 key 失效的一瞬间 大量请求密集访问导致的缓存击穿,但这样就要考虑要存储的数据量的大小和 redis 服务实例可以存储的大小,做好冷、热数据的区分处理,冷数据还是做定时失效,不然冷数据就会浪费缓存空间;
key 访问计数动态调整失效时间
实际可能会有这种情况:就是我们没办法提前知道哪一个 key 会是热点数据,针对这种情况,我们可以为这些数据增加一个算法实现——计数单个 key 在单位时间内的访问频率,当高到一个阈值之后,我们把这个 key 设置为永不过期。
加锁排队
public List<ProductCategory> findProductCategory() {
String key = "product:product-category";
Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (obj == null) {
synchronized (this) {
/*
因为有可能存在这样的情况:
请求A执行完了
List<ProductCategory> productCategories = productCategoryMapper.selectProductCategory();
将要执行
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, productCategories, Duration.ofHours(2));
但还未执行
请求B(也可能是其他多个请求)执行完了
Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (obj == null) {
将要执行
synchronized (this) {
但还未执行,
就会出现多次 从数据库查询、更新到缓存的情况
所以进入 synchronized 一定要再查询一次 Redis,这样可以避免多次查询数据库、更新缓存
*/
obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (obj != null) {
return (List<ProductCategory>)obj;
}
List<ProductCategory> productCategories = productCategoryMapper.selectProductCategory();
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, productCategories, Duration.ofHours(2));
return productCategories;
}
} else {
return (List<ProductCategory>) obj;
}
}
既相对简单又比较彻底的方案还是加锁排队。
缓存雪崩
是缓存中的 key 大量集中过期(或缓存服务器宕机),导致大量请求访问数据库,造成数据库瞬间压力过大,宕机。
区别于缓存击穿的是:缓存击穿指的是大量并发请求集中访问一个 key 时,key 不在缓存里时出现的情况;缓存雪崩则是因为大量 key 在时间上集中过期或不存在时,面对大量并发请求的访问都要去查数据库时发生的情况。
解决方案
在加锁排队的基础上,设置随机失效时间
public List<ProductCategory> findProductCategory() {
String key = "product:product-category";
Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (obj == null) {
synchronized (this) {
/*
因为有可能存在这样的情况:
请求A执行完了
List<ProductCategory> productCategories = productCategoryMapper.selectProductCategory();
将要执行
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, productCategories, Duration.ofHours(2));
但还未执行
请求B(也可能是其他多个请求)执行完了
Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (obj == null) {
将要执行
synchronized (this) {
但还未执行,
就会出现多次 从数据库查询、更新到缓存的情况
所以进入 synchronized 一定要再查询一次 Redis,这样可以避免多次查询数据库、更新缓存
*/
obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
if (obj != null) {
return (List<ProductCategory>)obj;
}
List<ProductCategory> productCategories = productCategoryMapper.selectProductCategory();
int seconds = (int) (Math.random() * 100);
Duration expire = Duration.ofHours(2).plus(Duration.ofSeconds(seconds));
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, productCategories, expire);
return productCategories;
}
} else {
return (List<ProductCategory>) obj;
}
}
实现让缓存失效的时间分散,就避免了缓存集中失效导致的缓存雪崩。
缓存服务高可用
实现缓存服务高可用,使用 redis 的哨兵模式,当某个 redis 实例异常、宕机时其他缓存服务实例迅速补位
缓存穿透
缓存中不存在、数据库中也不存在的数据,导致每次请求都会查询数据库,高并发访问这种数据的请求很可能是攻击者。
比如发起 id 为“-1”的数据,或者 id 特别大(数据库中不存在的数据),导致数据库压力过大或宕机
解决方案
缓存空对象
这个方案就是使缓存中存储对应 key 的值为空(空字符串或其他代表空的值),查询缓存直接取到空值返回。
这个方案的缺点就是如果查询的 key 值一直变的话,空 value 的缓存也会有很多占据缓存空间。
布隆过滤器
这个是比较彻底的解决方案了,利用 bitmap 数据结构存储数据在数据库中是否存在的信息
如果 bitmap 返回不存在,那么就一定不存在;
如果 bitmap 返回存在,那么就概率存在;
注意:使用布隆过滤器需要在服务器启动阶段进行数据初始化加载,比如对于 id,在对外提供新增记录的功能前先将所有的 id 都加载到布隆过滤器中,之后每一次 insert 之后都要将 id 加入布隆过滤器。
redisson 中有对布隆过滤器的现成封装可以直接使用:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.redisson</groupId>
<artifactId>redisson-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.16.1</version>
</dependency>
public ExpressInfo findByDeliveryOrderId(Long id) {
RBloomFilter<Long> bloomFilter = redissonClient.getBloomFilter("xushu-product:bloom-filter:express-info");
if (!bloomFilter.contains(id)) {
throw new ClientException("发货单:{} 的物流信息不存在", id);
}
String key = "xushu-express:express-info:";
//从 Redis 查询物流信息
Object obj = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key + id);
if (obj != null) {
return (ExpressInfo) obj;
} else {
ExpressInfo expressInfo = expressMapper.selectByDeliveryOrderId(id);
if (expressInfo != null) {
bloomFilter.add(id);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key+id, expressInfo, Duration.ofHours(2));
return expressInfo;
} else {
throw new ClientException("发货单:{} 的物流信息不存在", id);
}
}//end else
}
也可以自行实现,
注意:redisson 的开源版本没有做集群布隆过滤器的实现,pro 版本有要付费……https://redisson.pro/