“C语言中的宏常量”的版本间的差异
跳到导航
跳到搜索
Jihongchang(讨论 | 贡献) |
Jihongchang(讨论 | 贡献) |
||
| 第40行: | 第40行: | ||
|} | |} | ||
hello.i 这个预处理文件就出现了。 | hello.i 这个预处理文件就出现了。 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | 在 hello.i 中 “ctrl+l”找到 main 函数,能看到宏常量已经被替换:<syntaxhighlight lang="console"> | ||
| + | int main() | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | int a = 100; | ||
| + | float r = 10, s = 0; | ||
| + | s = r * r * 3.14; | ||
| + | printf("s = %f \n", s); | ||
| + | return 0; | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
2022年10月28日 (五) 10:29的版本
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1vR4y1H7MY/?p=10
C语言的常量分为
- 字面常量
- 用 #define 定义的宏常量:可以用 #define 定义一个标识符来表示一个常量。其特点是:定义的标识符不占内存,只是一个临时的符号,预编译后这个符号就不存在了。
- 用 const 关键字修饰的变量,称为常变量
- 枚举常量
- 字符常量和字符串常量
#include<stdio.h>
#define LEN 100
#define PI 3.14
int main()
{
int a = LEN;
float r = 10, s = 0;
s = r * r * PI;
printf("s = %f \n", s);
return 0;
}
#define 只要一个作用,就是 替换。
#include 是 包含。
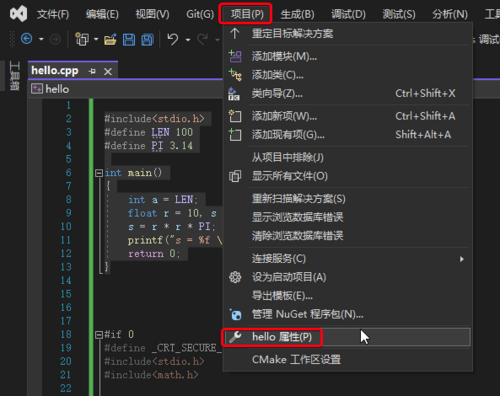
宏常量在预编译时进行替换:
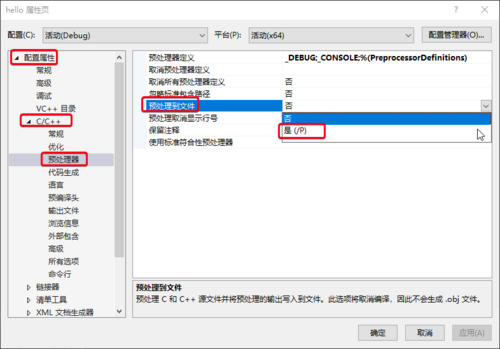
打开预处理到文件
然后“应用”“确定”
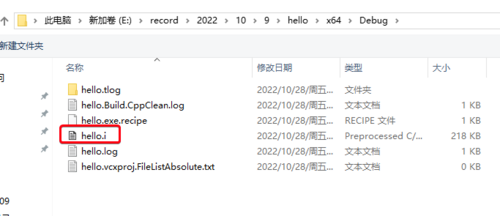
hello.i 这个预处理文件就出现了。
在 hello.i 中 “ctrl+l”找到 main 函数,能看到宏常量已经被替换:
int main()
{
int a = 100;
float r = 10, s = 0;
s = r * r * 3.14;
printf("s = %f \n", s);
return 0;
}